나의 발자취
[Two Pointers] 15. 3Sum 본문
문제 링크 https://leetcode.com/problems/3sum/description/
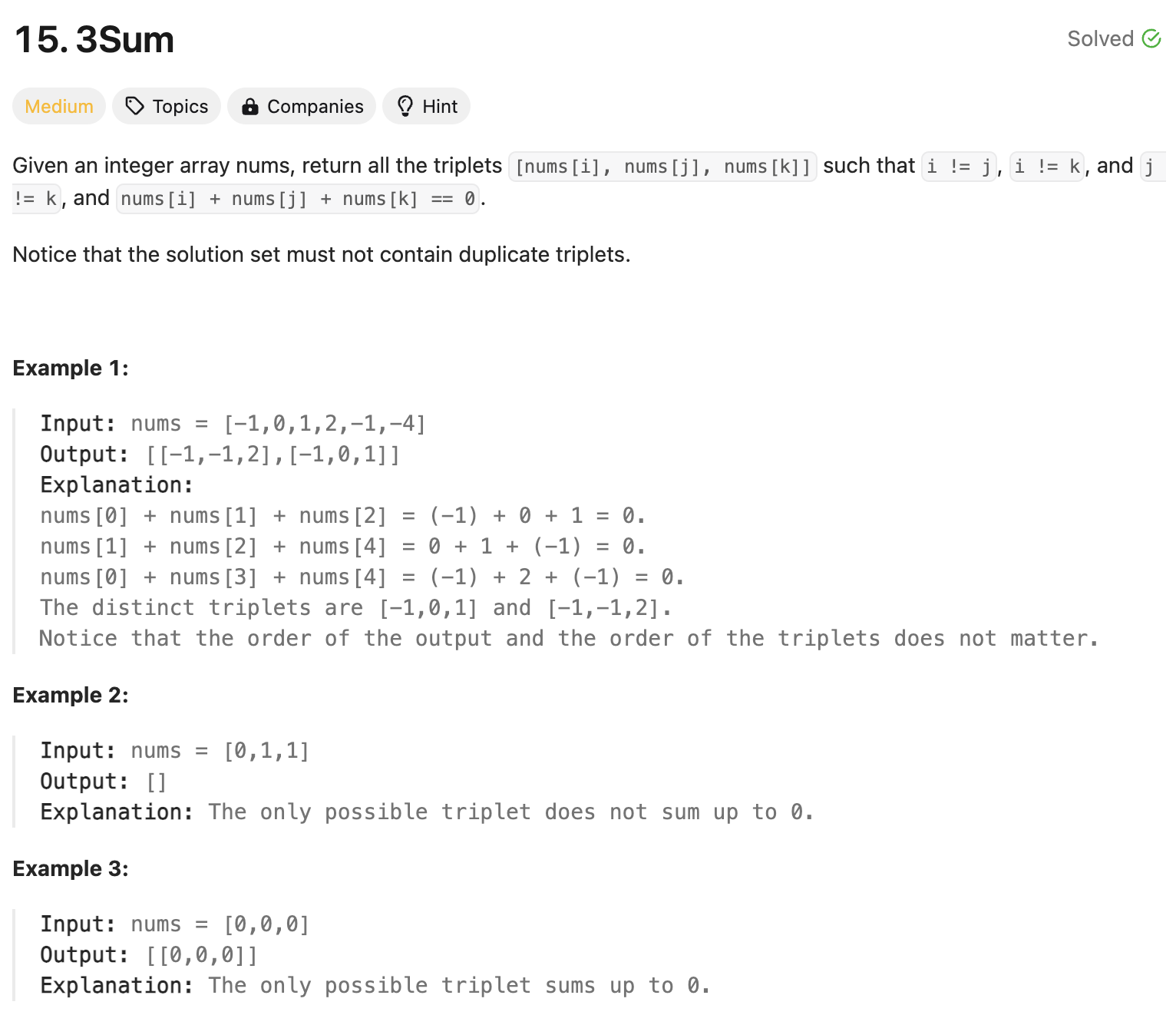

문제 접근 방법
투포인터임. 무조건~ 근데 중복 값 처리가 은근 까다롭다.
1. 일단 처음은 배열을 정렬해서, 중복되는 값들을 처리하기 쉽게 하는데 이렇게 되면, 중복된 값들이 정렬된 배열에 서로 연속으로 놓여있기 때문에 스킵하기 편하고, 이 결과 유니크한 triplet을 답으로 확보할 수 있다.
2. 그다음은 순회를 할건데, 각 순회마다 "피벗"이 되는 nums[i]를 두고 그 오른쪽의 값들(추후 투포인터가 됨)이랑 비교를 계속 하는거다. 목표는 투포인터의 합이 -nums[i]가 되면 된다.
그래서 만약에 합이 너무 크면 right 포인터를 왼쪽으로, 작으면 left 포인터를 오른쪽으로 옮기면서 하면 되고, 만약 합이 0이라면 triplet을 result에다가 담으면 된다.
- Sort the input array, nums, in ascending order.
- Create an empty list, result, to store the unique triplets.
- Use a for loop to iterate over the array, treating each element nums[i] as the pivot.
- Start the iteration at index 0 until the third-to-last element inclusive (because at least three elements are needed for a triplet).
- Initialize two pointers:
- low starts at i + 1 (the element after the pivot).
- high starts at the last element of the array.
- While low is less than high, compute the sum of the pivot,nums[low], and nums[high]:
- If the sum is less than zero, increment low to increase the sum.
- If the sum is greater than zero, decrement high to decrease the sum.
- If the sum equals zero:
- Add the triplet [nums[i], nums[low], nums[high]] to the result.
- Move both pointers to their next positions (low++ and high--).
- Skip duplicates at the new low and high positions to ensure unique triplets.
- If nums[i] == nums[i - 1] (for i > 0), skip the current iteration.
- If nums[i] > 0, break the loop. (위에서 nums[low] + nums[high] == -nums[i] 을 찾는 것이기 때문에 pivot은 양수여야만 한다. 그러나 세 개의 값의 합이 0인 경우로 조건을 달리 한다면, 이러한 별도의 break문은 필요없다)
- Initialize two pointers:
- Once the loop completes, return the result list containing all unique triplets.
Let’s look at the following illustration to get a better understanding of the solution:
고민한 부분 & 주의사항
투포인터지만 인덱스는 3개이다 보니, 조건을 작성할 때 조금 까다로웠다.
일단 for loop의 current 인덱스의 레인지부터 시작해서,
중복된 값들이 나올 수 있는 경우를 생각해야했는데, 가령 current 인덱스가 또 같은 값을 가리킬 때라던가, 투 포인터 인덱스에도 또 똑같은 값을 가리키면 답이 중복으로 나올 수 있기 때문에 이 부분을 하는게 조금 까다로운 정도.
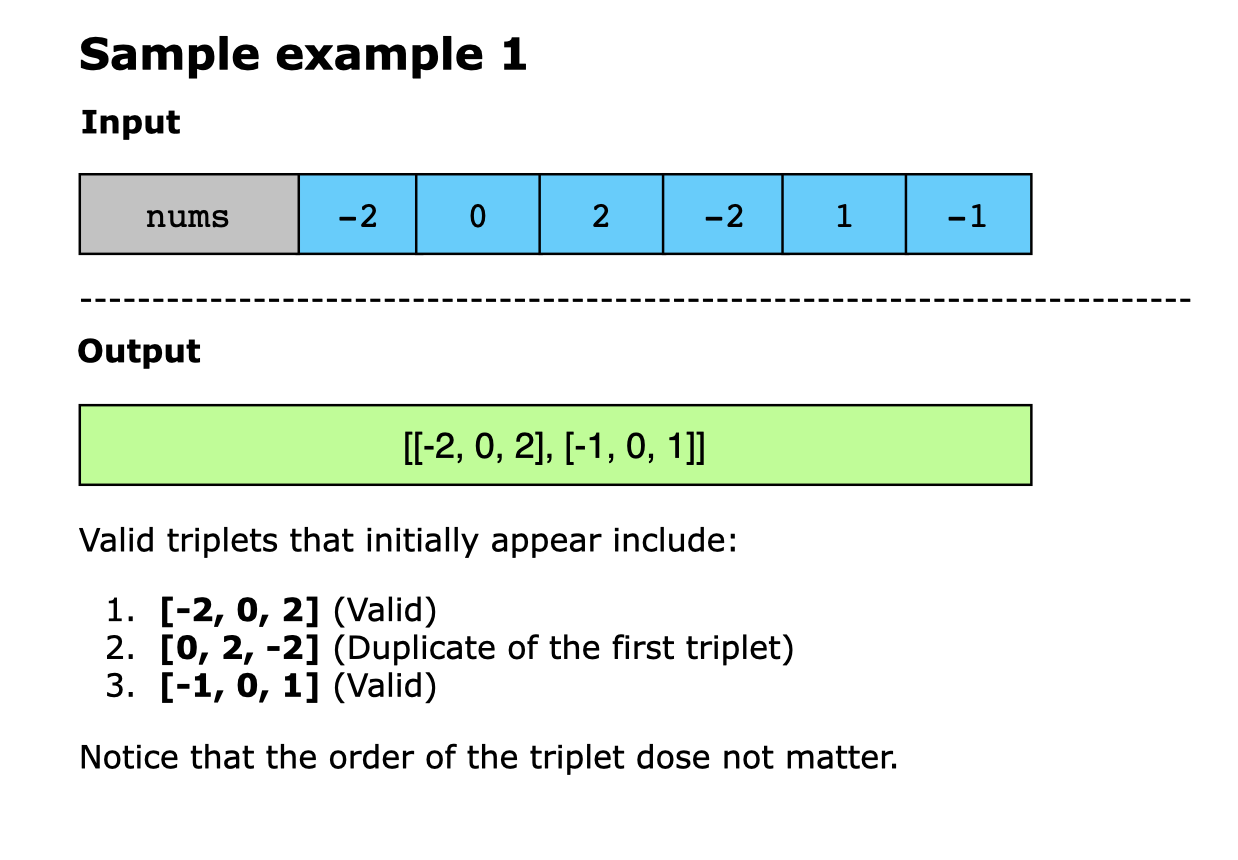

중복 처리를 하지 않으면, 위와 같이 결과값이 중복되게 된다. 따라서, 코드 구현상에서는 중복되는 값을 스킵해주어야한다.
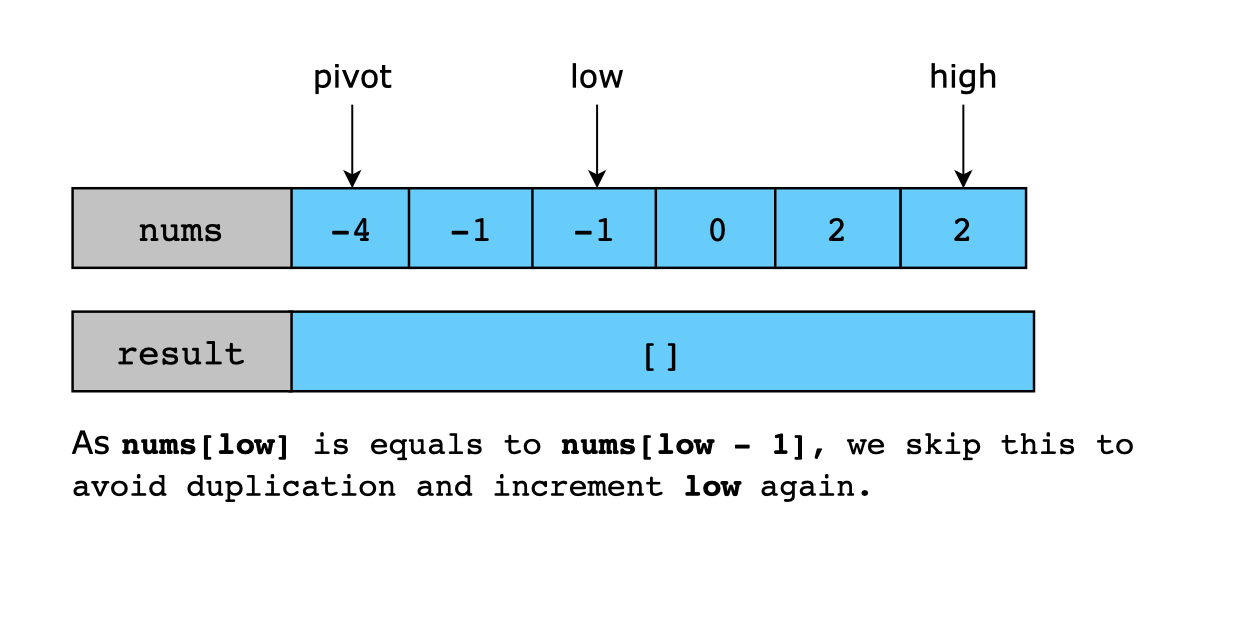
코드
1) sum = nums[cur] + nums[left] + nums[right]이라고 정해놨을 때
class Solution:
def threeSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
nums.sort()
arr = []
for cur in range(len(nums) - 2):
if cur > 0 and nums[cur] == nums[cur - 1]:
continue # skip duplicates
left, right = cur + 1, len(nums) - 1
while left < right:
sum = nums[cur] + nums[left] + nums[right]
if sum < 0:
left += 1
elif sum > 0:
right -= 1
else:
arr.append([nums[cur], nums[left], nums[right]])
left += 1
right -= 1
# skip duplicates
while left < right and nums[left] == nums[left - 1]:
left += 1
while left < right and nums[right] == nums[right + 1]:
right -= 1
return arr
2) nums[low] + nums[high] == -nums[i] 일 때
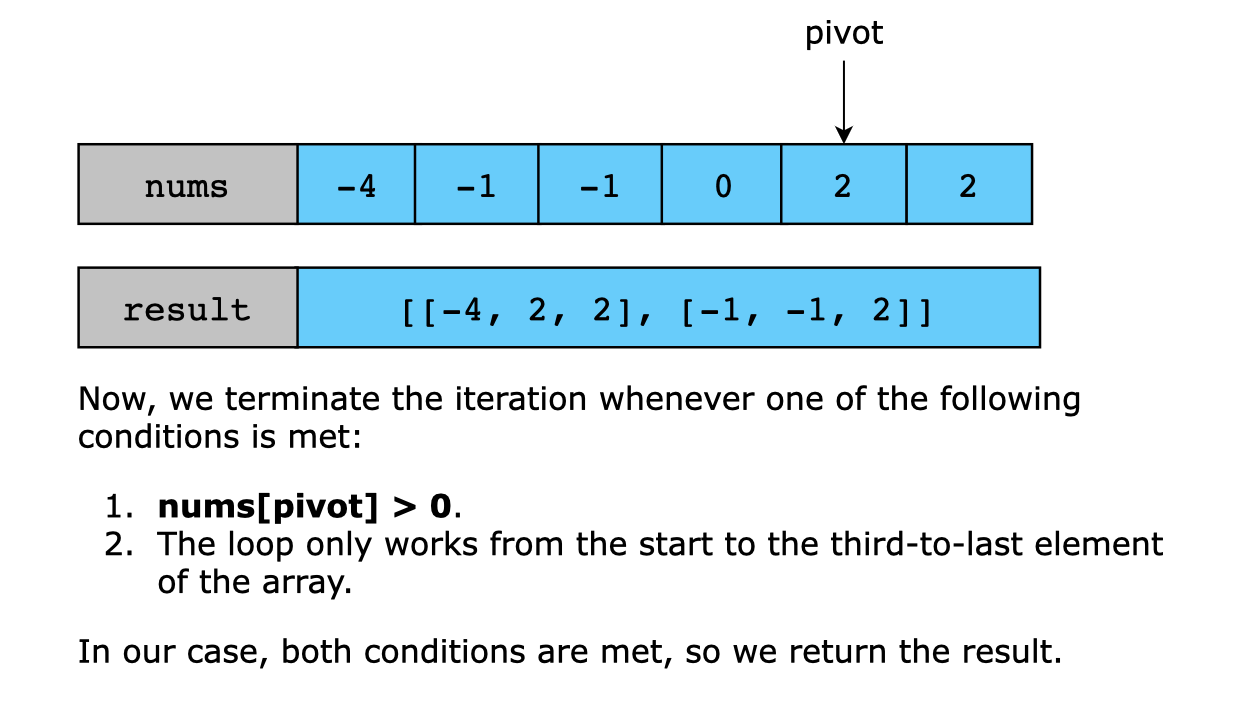
def three_sum(nums):
nums.sort()
result = []
n = len(nums)
for pivot in range(n - 2):
if nums[pivot] > 0:
break
if pivot > 0 and nums[pivot] == nums[pivot - 1]:
continue
low, high = pivot + 1, n - 1
while low < high:
total = nums[pivot] + nums[low] + nums[high]
if total < 0:
low += 1
elif total > 0:
high -= 1
else:
result.append([nums[pivot], nums[low], nums[high]])
low += 1
high -= 1
while low < high and nums[low] == nums[low - 1]:
low += 1
while low < high and nums[high] == nums[high + 1]:
high -= 1
return result
반복밖에 없다 ^^
Time complexity
시간 복잡도는 O(n²)이다.
- Sorting: sort()에서 O(n logn)
- Two pointers: nested iteration 이므로, O(n²) 이 된다.
Space complexity
공간 복잡도는 O(n)이다.
- Sorting: sort()에서 O(n)
- Two pointers and result storage: 투포인터는 배열 내부에서 일어나고, 결과값은 triplets의 개수에 따라 달라지는데 보통 input 입력의 크기보다 훨씬 작다.
'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Two Pointers] 19. Remove Nth Node From End of List (0) | 2025.02.13 |
|---|---|
| [Two Pointer, ::] 125. Valid Palindrome (0) | 2025.02.13 |
| Two Pointers 기법이란? (Why / When / How to use) (0) | 2025.02.13 |
| 334. Increasing Triplet Subsequence (0) | 2025.01.30 |
| [그리디] 605. Can Place Flowers (2) | 2025.01.04 |




